The municipal bond market is currently displaying mixed signals amidst significant macroeconomic factors influencing investor behavior. As participants await decisions from the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), it is crucial to analyze how recent developments are shaping the landscape for tax-exempt and taxable bonds. This article delves into recent trends in municipal bonds, contrasts performance against other asset classes, and reviews new offerings while providing insights into potential future movements.
As investment activity in the municipal bond arena remains steady, the backdrop of falling U.S. Treasury yields has set the stage for a complex narrative. Cooper Howard, a fixed-income strategist at Charles Schwab, highlighted an emerging consensus that a rate cut by the Federal Reserve is almost certain in the upcoming meeting. However, the intricacies of how deeply the rates will be slashed remains a matter of intense debate. Such monetary policy adjustments are critical to influencing bond prices; a cut typically enhances the attractiveness of municipal bonds, which, when adjusted against expected returns, presents a generous opportunity for appreciation.
“The Fed’s anticipated rate cuts are likely to drive a positive price trajectory for both taxable and tax-exempt bonds,” asserted Matt Fabian from Municipal Market Analytics. This statement underscores a vital correlation between Fed policy and the yield environment for municipals. Many investors now see prospects for increased performance given that current nominal yields are notably higher than when the Fed’s stance was characterized as dovish.
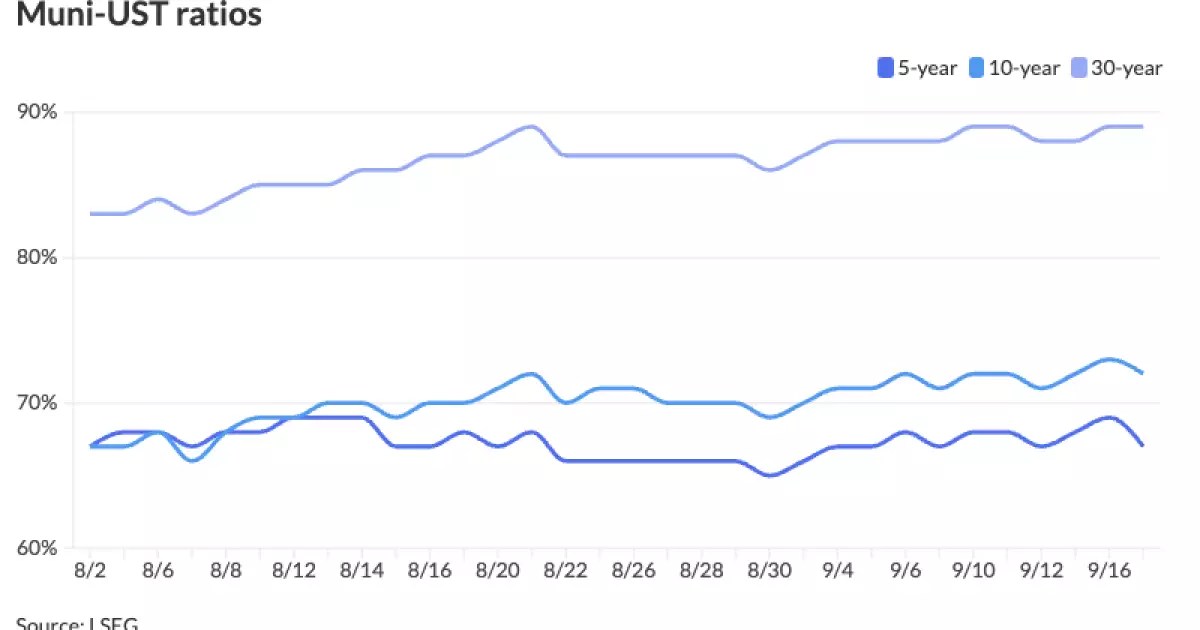
Despite the positive outlook shared by some industry experts, a close examination of historical performance reveals that municipal bonds have lagged behind their U.S. Treasury (UST) and corporate counterparts. Year-to-date, municipal bonds have returned only 2.04%, significantly trailing UST returns of 2.98% and corporate returns of 5.87%. Such underperformance may raise concerns among investors, but Howard points to a silver lining: the relative valuations for municipal bonds have improved across various maturities. For instance, the muni-to-Treasury ratio has shown a stabilizing trend, hovering around 70% for bonds with maturities less than ten years.
While the recent uptick in relative valuations may be deemed attractive, the caution advised by analysts remains relevant. Despite a surge in 2a7 assets of $40 billion, there is skepticism surrounding the immediate redirection of funds from money market holdings to municipal investments. Investors, particularly those focused on income-oriented separately managed accounts (SMAs), may be slow to pursue lower tax-exempt yields, particularly before the influence of Fed decisions become clearer.
Recent activity in the primary market highlights the robust appetite for municipal bonds, reflected in a series of major new issue offerings. For example, J.P. Morgan’s pricing of $476.585 million in electric system revenue bonds underscores a significant commitment by institutional investors. These bonds—spanning several tranches with varying maturities—demonstrate an active engagement by issuers to capitalize on current market conditions.
In addition, notable issuances from the Public Power Generation Agency and the New York City Housing Development Corporation indicate that demand for socially responsible investment is also strong. Taxable and tax-exempt bonds are attracting varied investor segments, further underscoring the multifaceted nature of the current market.
Moreover, the competitive environment remains rife with opportunities as Illinois opened several offerings, including both tax-exempt general obligation bonds and taxable series. Such activities indicate robust investor engagement across different credit ratings and bond types, enhancing liquidity in the municipal market.
With the dynamics of the municipal bond market unfolding amid potential Fed policy shifts, the outlook remains cautiously optimistic. The expected price appreciation brought on by rate cuts could bolster investor confidence, particularly if the market responds favorably to a more favorable yield landscape. Nevertheless, investors are faced with important challenges, including the need to balance risk and returns amidst the prevailing underperformance relative to other asset classes.
As market participants look toward the horizon, the once-for-sure increase in demand for tax-exempt bonds could transform quickly once the Fed’s decisions materialize. Given the uncertain trajectory of inflation and economic recovery, investors must remain vigilant, monitoring both macroeconomic indicators and strategic issuance movements in the municipal bond market.
The municipal bond market is at a crossroads—forecasting strong performance driven by anticipated rate cuts while simultaneously grappling with persistent yield competition. With careful analysis and a proactive investment strategy, stakeholders can navigate this complex landscape, forging pathways for robust returns in the ever-evolving world of municipal finance.

Leave a Reply